| |
Introduction: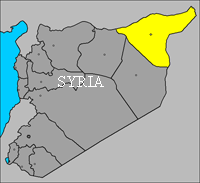
Al Hasakah Governorate It is situated in the far North-East of the Syrian Arab Republic.
It's about 23.300 k.m2. Its population is more than 1.050.000 persons. It is distinguished by the fertility of its lands, plentiness of water, beauty of nature and the muchness of its archaeological sites besides, its modern architectural and civilizational growth and its numerous and useful agricultural and industrial projects.
The most important river in Alhasaka is Alkhabour river which springs from Ras Alayn, goes east toward Al-Hasaka, then goes south to meet the Euphrates at Albsiera (Karkisia) in Dier Azzor after passing Al-Hasaka governorate for about 440 km. Its stream forms islands called Alhawaiej which are exploited as parks.
The most Important Cities at Al Hasakah Governorate are:
Al Hasakah city: is the capital of the Al Hasakah Governorate. Al Hasakah has the second highest population in the governorate, 81,809, with the majority being Assyrians and Kurds. The town lies on the banks of the Khabur River (a tributary of the Euphrates) at its confluence with the Jaghjaghah.
It's characterized by the beauty of site, its modern architectural and civilizational growth, and the different activities. There are factories, economical projects, touristic institutions, and different sport, cultural and educational activities.
Under the Ottoman Empire it lost its importance, but it revived with the settlement there of Assyrian refugees from Iraq during the French mandate of Syria after 1932. Now an important road junction near the Turkish and Iraqi frontiers
Alqameshli city: It's characterized by its straight streets, different activities, touristic institutions and airport.
Almalkieh city: It's characterized by the beauty of nature and the muchness of springs. It contains the archaeological bridge goes back to 3th AC.
Also, there are important oil wells.
Ras Alayn: It looks like a floating city on a lake of springs. There are, also, mineral springs. Many well known persons in the history of civilization came out of it.
Ayn Diwar: It looks out on Dejlah River. It contains the remains of the archaeological bridge.
Around Al Hasakah
Tall Birak (Najar): Ancient site located in the fertile Nahr al-Khabur basin in Al-Hasakah governorate, Syria; it was inhabited from c. 3200 to c. 2200 BC. One of the most interesting discoveries at Birak was the Eye Temple (c. 3000), so named because of the thousands of small stone “eye idols” found there.
Tall Birak is situated between Al-Hasaka and Al-Qameshli. The dig started in 1937 – 1939. It was resumed after the 1st World War. It showed six successive civilizational layers. King Naram Sin palace and Al-Ayoun temple were the most important discovered buildings. Also, there are clay findings, statues and cylindrical stamps which are rich in their mythological subjects. civilizational layers. King Naram Sin palace and Al-Ayoun temple were the most important discovered buildings. Also, there are clay findings, statues and cylindrical stamps which are rich in their mythological subjects.
Tall Halaf (Gozana): In the south of Ras Al'ain city, the dig revealed many successive civilizational layers and beautiful basaltic statues which decorated. the walls of the temple and the palace. Its clay was known as (Halaf hill clay).
Tall Ajaja (Araban): It's situated to the south of Al-Hasakah. It was an important centre on the borders area between the Roman and Persian Empire. The old city, whose ruins are in this hill, was one of the most cities in Alkhabour Bed in the Abbasyeen Era.
Tall Shagher Bazar (Huteen): It's situated in the north of Syria. The dig began in 1934. And it is still continuing. It revealed 15 successive civilizational layers. Its findings, clay plates, had supplied us by useful information in the study of the history of the ancient east and its civilizations.
Tall Lilan (shbat Enlil): It's situated in the south of Al-qameshli; about 25 km. at Alkhabour triangle area. The dig began in 1978. It revealed layers which go back to 6000 B.C, the wall of the city, buildings such as: the temple and the palace, clay plates, cylindrical stamps, and various fictile ruins. All that made Lilan hill one of the most important archaeological hills.
Tall Barri (Kaht): It's situated on the eastern edge of Jaghjagh River. It's situated 8 km far from Brak hill to the north. Tow important archaeological carvings were found which helped recognizing the name of this site (Kaht). It was the last stage of The Assyrian King's (Tokotly Ninorta) conquest across the lands of Al-Jazeera in 885 B.C. His tracks showed its importance.
Tall Mozan ( Orkiesh): It's situated between Amoda and Alqameshli city. It includes an archaeological city. At the beginning of 2000 B.C., the dig revealed the city wall, the remains of stone building, stamps and important different ruins.
Tall Alkhwieri: Between Ras Alayn and Tal Abiad, the dig revealed an important stone temple, buildings and fictile, metal and bony findings. The Acadian ax is considered one of the most important finding. Also, there are many important archaeological places such as Alamara hill, Baider hill and the Ayyobian castle which is about 35 km far from Al-Hasaka and situated on the northern side of Abd Alaziz Mountain.
|
|




 civilizational layers. King Naram Sin palace and Al-Ayoun temple were the most important discovered buildings. Also, there are clay findings, statues and cylindrical stamps which are rich in their mythological subjects.
civilizational layers. King Naram Sin palace and Al-Ayoun temple were the most important discovered buildings. Also, there are clay findings, statues and cylindrical stamps which are rich in their mythological subjects.